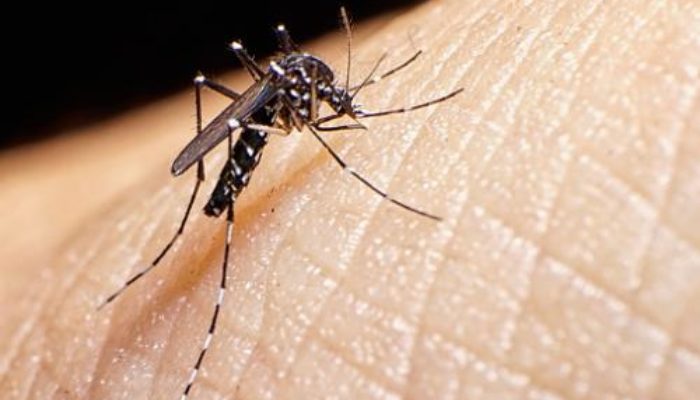
Dengue or “Break bone fever” is a severe, flu-like illness caused by a virus in the blood. It may prevent the blood from clotting properly, and cause bleeding.
Dengue should be suspected when a high fever (40°C/104°F) is accompanied by 2 of the following symptoms: severe headache, pain behind the eyes, muscle and joint pain, nausea, vomiting, swollen glands or a rash. This is known as the “dengue triad.”
How do people contract Dengue?
Dengue is carried by the Aedes mosquito. The mosquito takes blood from one infected person, and then carries the infection to another person. These mosquitos are identified by the black and white stripes on their bodies. Their peak biting periods are early in the morning and in the evening before sunset.
Treatment: There is no vaccine or specific medicine for dengue.
- Take paracetamol for fever and pain
- DO NOT take aspirin or ibuprofen.T
- They will thin the blood and may result in bleeding
- Drink lots of fluid— water, juice, soup
- Get lots of rest
In most cases, the fever eventually goes away by itself.
After 2 to 7 days of dengue fever, some people develop a severe complication called Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF). This is dengue fever with bleeding and needs urgent medical care. Proper medical attention is needed to avoid complications and risk of death. Seek medical help right away if any of these signs appear within 24 hours after the fever is gone:
- severe abdominal pain
- continuous vomiting
- rapid breathing
- bleeding gums
- tiredness
- restlessness
- blood in vomit (brown colour), urine (tea colour) or poop (black colour)
Prevention
Do not give mosquitoes places to breed. Frequently check and remove stagnant water in your home. Prevent mosquito bites by using windows and door screens in your homes and using safe mosquito repellent sprays. Prevention is better than cure.
Source: WHO/ Dengue and severe dengue (http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs117/en/)